The software event brokers provide the data path functionality to allow applications to communicate in real time. An event broker service in advanced event mesh for SAP Integration Suite is made up of either a standalone software event broker (
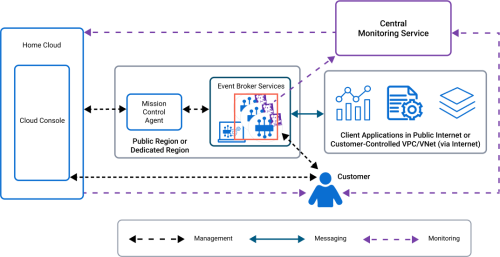
In the following diagram, the red box highlights event broker services. Each service has a Datadog agent that collects statistics and logs from it. The Broker Manager is used to connect to the event broker service. For information about the data exchanged, see Information Exchanged Between the Event Broker Services and the Centralized Monitoring Service.
Event Broker Services Designed for Reliability
In the unlikely situation that the active broker fails, the standby broker takes over automatically; this permits for faster recovery in the event of a failure.
Event broker services are centrally managed by a customer from the Mission Control in the Cloud Console and is actively monitored by SAP. For Enterprise services, the event broker service's status, high-availability readiness, and Config-Sync status are all monitored by SAP using metrics and log data. This permits for alerts to SAP and helps to enable rapid response. These readiness alerts are also available to you if you subscribe to the Insights.
Event broker services operate independently from
Information Exchanged Between the Event Broker Services and the Centralized Monitoring Service
SAP uses the Datadog cloud application for its central monitoring service component. The Datadog agent is the monitoring component that resides in a deployment. There is one Datadog agent per event broker service. The Datadog agents collect and send monitoring information from the event broker services to the central monitoring service (Datadog). For more details about the central monitoring service, see Central Monitoring Service and Datadog Agents.
Connectivity Between Event Broker Services and Client Applications
Client applications can publish and subscribe to messages when connected to an event broker service. Client applications connect to an event broker service using:
- the event broker service's generated hostname or a custom hostname
- Client Messaging APIs that communicate using specific protocols and over ports.
In cases when a custom hostname is required, the custom hostnames can be assigned to each event broker service to make deployment and integration with client applications easier. These hostnames can be reassigned to another event broker services to migrate the service. For more information about using custom hostnames to access event broker services, see Configuring Custom Hostnames for an Event Broker Service.
Client applications can only connect to ports that you configure when you create an event broker service. By default, when you create an event broker service, all secure ports and protocols are enabled. Plain-text ports are available for compatibility for legacy applications but are disabled by default.
After client applications connect to an event broker service using the available protocol and port, they must authenticate and be authorized to use the event broker service. For more information, see Client Applications for Messaging.
The following table lists the protocol ports, indicates whether the port is enabled by default when a event broker service is created, the protocol used for Messaging Connectivity (Data traffic).
| Port for Each Protocol | Enabled by Default for an Event Broker Service | Protocol and Description |
|---|---|---|
|
443 |
Yes |
Secured Web Transport TLS/SSL |
|
5671 |
Yes |
Secured AMQP |
|
8443 |
Yes |
WebSocket Secured MQTT |
|
8883 |
Yes |
Secured MQTT TLS/SSL |
|
9443 |
Yes |
Secured REST TLS / SSL |
|
55443 |
Yes |
Secured SMF TLS/ SSL (without compression) |
|
80 |
No |
Web Transport |
|
1883 |
No |
MQTT (plain-text) |
|
5672 |
No |
AMQP (plain-text) |
|
8000 |
No |
MQTT / WebSockets (plain-text) |
|
9000 |
No |
REST (plain-text) |
|
55003 |
No |
SMF-compressed |
|
55555 |
No |
Solace Message Format (SMF) - plaintext |
Outbound Connections Initiated by Event Broker Services
Event Broker Services can initiate oubound connections for RDP (REST) endpoints, or to other event broker services required for various features of SAP, such as Dynamic Message Routing (DMR) required for event mesh or VPN Bridge Links.
The following table lists the details for outbound connections, that is, connections initiated by event broker services to external event broker services (external brokers) or REST Delivery Points (RDPs)
| Connection |
Port
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|
| Brokers to External Brokers or REST endpoints |
Various ports (e.g., 55555, 55003, 55443, 9000, 9443, 8443, 8883, 8000, 1883, 5671, 5672, 443, 80, 1943, 55543, 943, 22) and are configured on a specific event broker service |
Required for outbound connections initiated by the event broker to RDP (REST) endpoints, or another event broker service (or event brokers) for features such as Dynamic Message Routing (DMR) for event meshes or VPN Bridge Links. |
Considerations About Event Broker Services
By default, event broker services are created to be secure. To balance ease of development with security, the defaults are as follows:
- all secure protocol and ports are configured with default port numbers
- a client profile named default is created that uses basic authentication
- plain-text ports are disabled but can be enabled for developer testing and characterizing traffic. SAP recommends that plain-text ports are not enabled in production.
These defaults are secure by default and recommended for use in production. You can further harden security by disabling protocols that you don't use or changing the default client profile to use a different authentication scheme rather than basic authentication. For additional recommendations to further harden access to your event broker services, see Hardening Access to Event Broker Services.